Understanding Blockchain Technology: The Foundation of Digital Trust
The interconnected nature of blockchain technology
1. Introduction
Visualization of a decentralized network structure
Blockchain technology represents a revolutionary approach to storing and tracking data that’s transforming industries worldwide. Born from the creation of Bitcoin in 2009, blockchain has evolved far beyond cryptocurrencies. This decentralized system creates an immutable record of transactions, ensuring transparency and security across networks.
Key aspects:
- The evolution from Bitcoin to modern applications
- Basic principles of decentralization
- Impact on traditional business models
- Current market statistics and adoption rates
2. How Blockchain Works
Technical structure of blockchain systems
Distributed Ledger Technology
Every participant (node) in the network maintains a complete copy of the transaction history. This eliminates single points of failure and ensures data integrity through consensus.
Block Structure
- Block header (metadata)
- Transaction data
- Timestamp
- Previous block’s hash
- Nonce value
Consensus Mechanisms
- Proof of Work (PoW)
- Proof of Stake (PoS)
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
- Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT)
3. Types of Blockchain
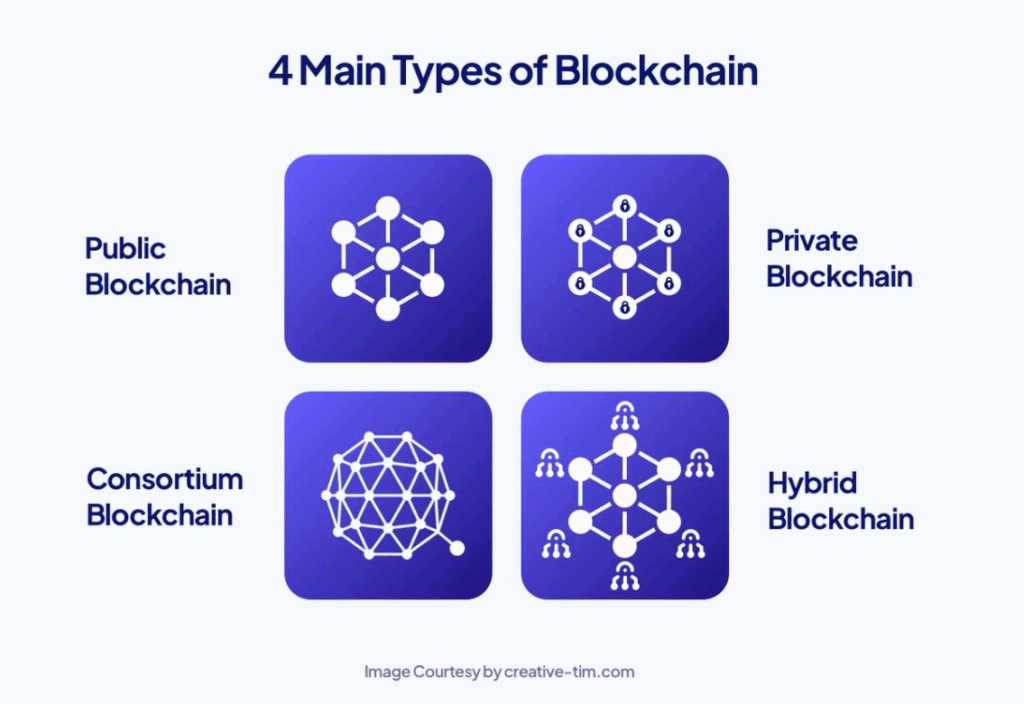
Public Blockchains
- Open, permissionless networks
- Examples: Bitcoin, Ethereum
- Complete decentralization
- Universal participation
Private Blockchains
- Controlled access
- Business applications
- Enhanced privacy
- Faster transactions
Consortium Blockchains
- Semi-decentralized
- Industry collaborations
- Shared governance
- Selective validation
4. Key Components
Essential components of blockchain technology
Smart Contracts
Smart contract implementation
- Self-executing contracts
- Automated enforcement
- Code-based rules
- Real-world applications
Nodes and Mining
- Types of nodes
- Network roles
- Validation processes
- Infrastructure requirements
5. Applications
Financial Services
Blockchain in financial services
- Traditional banking integration
- Investment platforms
- Insurance automation
- Asset tokenization
- Cross-border transactions
Supply Chain
Supply chain tracking and management
- Product authenticity
- Real-time tracking
- Supplier verification
- Inventory optimization
Healthcare
Blockchain applications in healthcare
- Patient data management
- Drug supply verification
- Clinical trial management
- Insurance claims processing
6. Benefits
Key advantages of blockchain technology
- Transparency
- Security
- Immutability
- Decentralization
- Cost reduction
7. Challenges and Limitations
Current challenges in blockchain implementation
- Scalability issues
- Energy consumption
- Regulatory concerns
- Integration with legacy systems
- Technical complexity
8. Future Trends
The future of blockchain technology
Emerging Trends
- Web3 integration
- NFTs and digital assets
- Metaverse integration
- Green blockchain solutions
- Cross-chain interoperability
Digital Transformation
The impact of blockchain on digital transformation
- Industry adoption
- New business models
- Innovation opportunities
- Future applications












